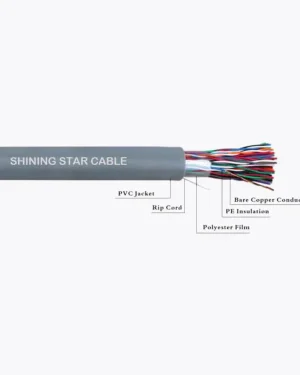
Characteristics of UTP
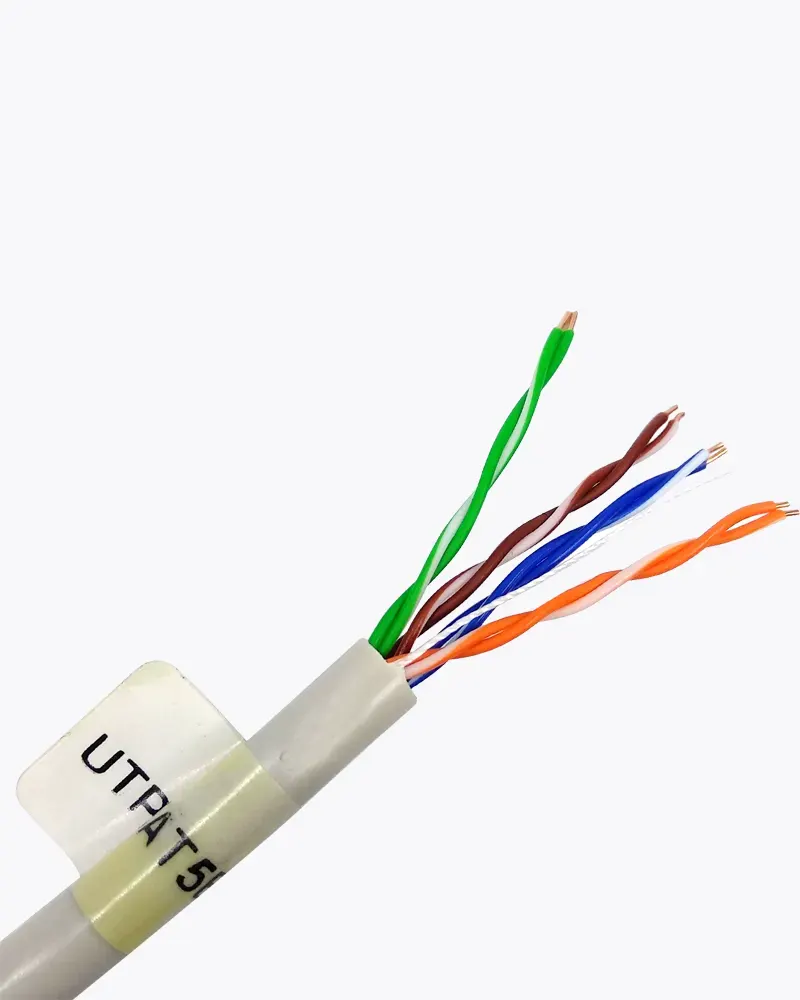
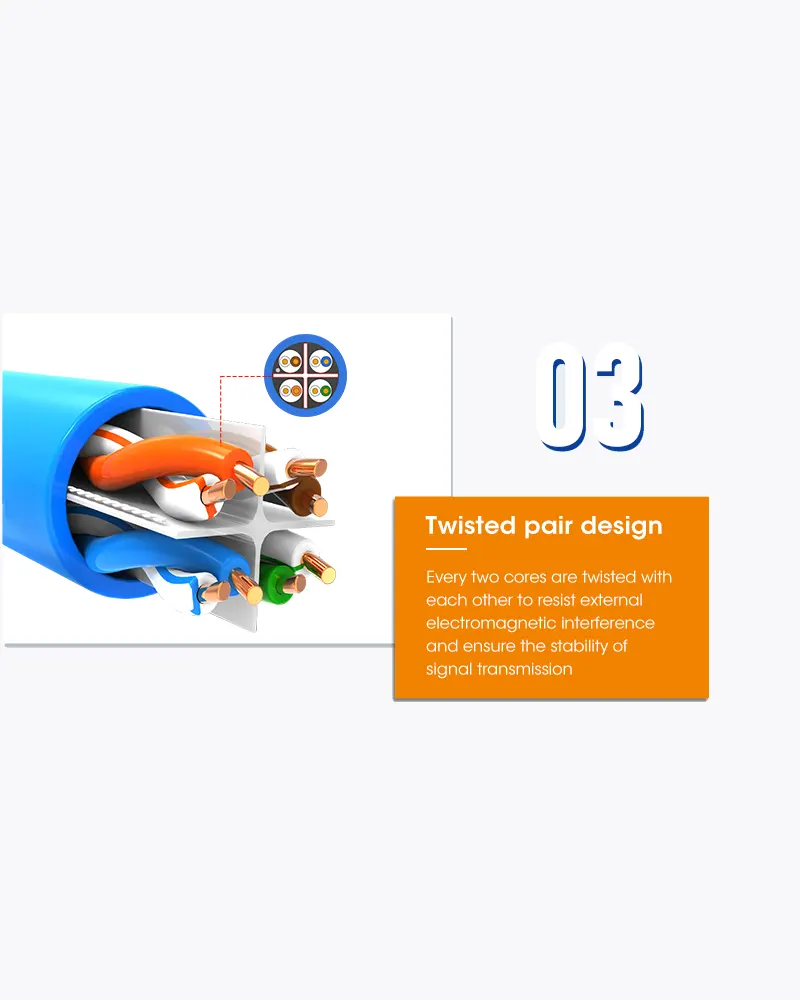
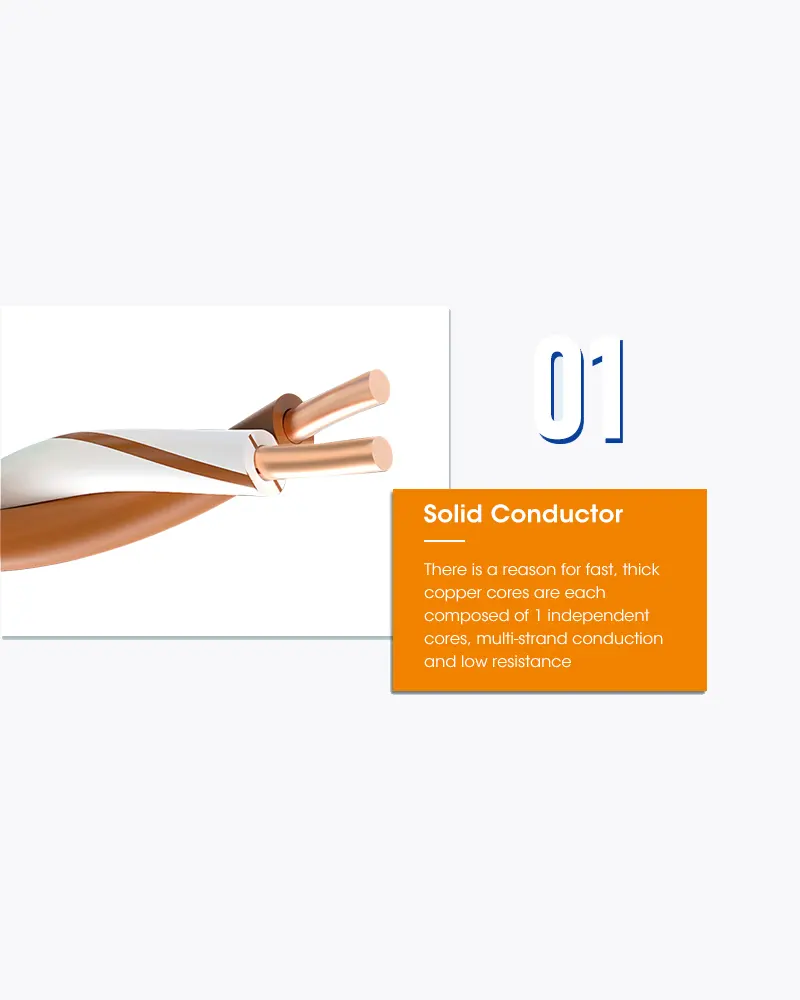
The characteristics of UTP are very good and make it easy to work with, install, expand and troubleshoot and we are going to look at the different wiring schemes available for UTP, how to create a straight through UTP cable, rules for safe operation and a lot of other cool stuff !
So let’s have a quick look at each of the UTP categories available today along with their specifications:
The more popular CAT5 wire was later on replaced by the CAT5e specification which provides improved crosstalk specification, allowing it to support speeds of up to 1Gbps. CAT5e is the most widely used cabling specification world-wide and unlike the category cables that follow, is very forgiving when the cable termination and deployment guidelines are not met.


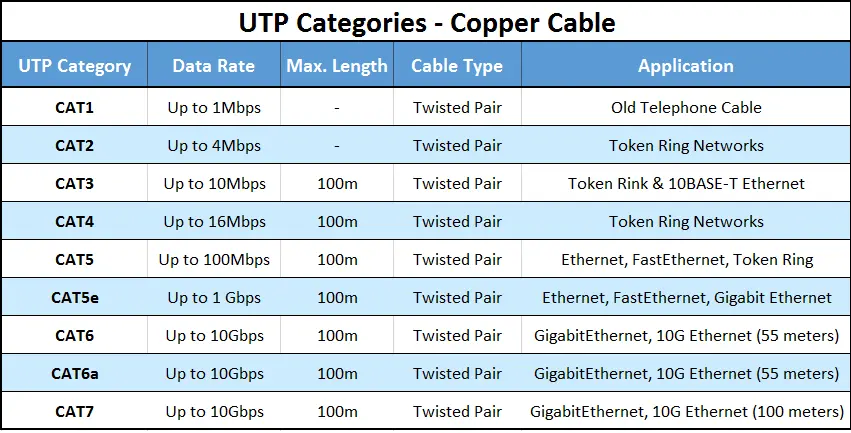
Category 1/2/3/4/5/6/7 – a specification for the type of copper wire (most telephone and network wire is copper) and jacks. The number (1, 3, 5, etc) refers to the revision of the specification and in practical terms refers to the number of twists inside the wire (or the quality of connection in a jack).
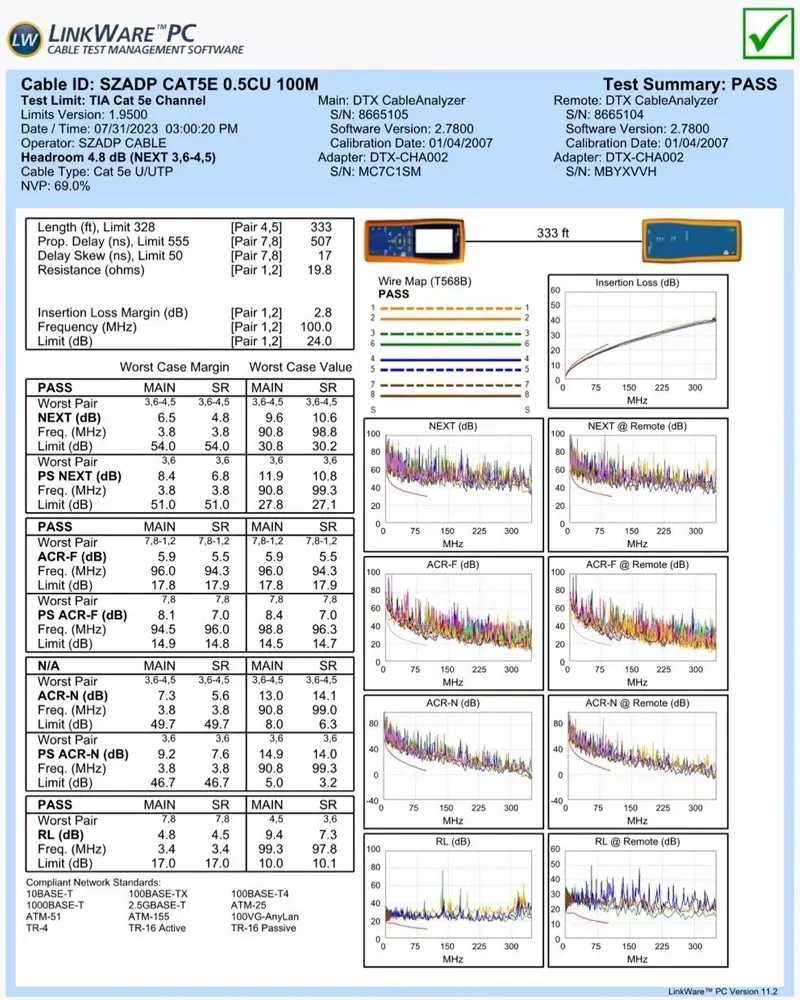
Electrical performance: Electrical Performance:
1.0-100.0MHZ Impendance(ohms)100±15
1.0-100.0MHZ Impendance Delay Screw(ns/100m)<45
Pair to ground Capacitance Unbalance(PF/100M)330 Max
Conductor DC resistance 20%(ohms/km)<93.8
Resistance Unbalance(%) 5